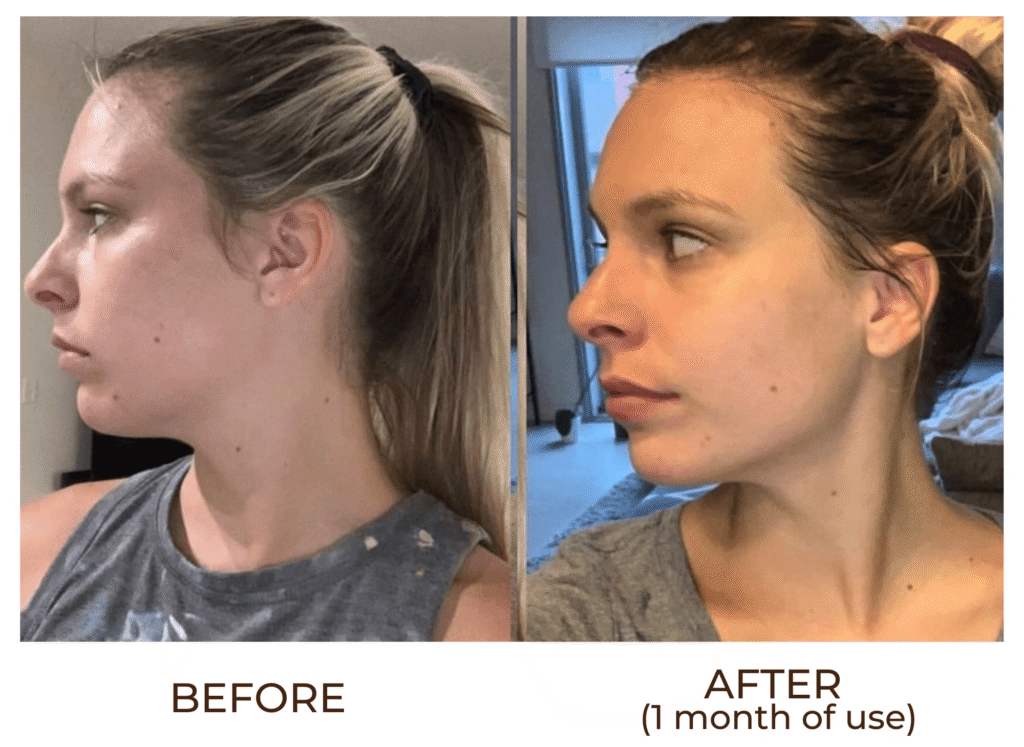
Abnormal Reactions After Gua Sha & Recovery Strategies: What You Should Know About This Popular Health Practice
With the rise of the internet, more and more people around the world have come to learn about gua sha. It is no longer confined to China or traditional Chinese medicine—gua sha has gone global and become a popular practice in modern wellness routines.
But have you ever experienced unusual symptoms gua sha after session?
Gua sha is not always risk-free. Every session may carry some degree of risk. Whether you’re a gua sha enthusiast or just planning to try it, understanding the potential abnormal reactions and knowing how to manage them is crucial.
Common Abnormal Reactions After Gua Sha
(Note: Not everyone will experience these symptoms)
- Fatigue and Weakness
This may occur due to excessive energy consumption. After Gua sha stimulates blood and energy flow, and your body may redirect energy toward recovery, leading to tiredness and a sense of weakness. - Dizziness, Nausea, and Palpitations
These may result from a weak constitution, excessive scraping pressure, or undergoing gua sha on an empty stomach. At such times, your body may lack sufficient energy to maintain normal function. - Severe Petechiae (Sha) with Redness or Blisters
This may be caused by either an allergic skin reaction or improper technique, especially if the scraping pressure is too strong. - Fever or Sudden Rise in Body Temperature
This can be a response of the immune system or inflammation triggered by after gua sha. Your body may raise its temperature to enhance immune function and fight harmful pathogens. - Emotional Fluctuations, Irritability, or Sudden Urge to Cry
These emotional responses may reflect a form of emotional release as understood in traditional Chinese medicine, or be related to nervous system stimulation. - Emotional Fluctuations, Irritability, or Sudden Urge to Cry
These emotional responses may reflect a form of emotional release as understood in traditional Chinese medicine, or be related to nervous system stimulation.
Recovery Strategies for Abnormal Gua Sha Reactions
- Stop gua sha immediately to prevent symptoms from worsening.
- Get adequate rest and allow the body to recover naturally; avoid intense physical activity.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a light, nutritious diet to help restore energy and blood flow.
- For severe skin redness or swelling, apply topical herbal treatments as needed.
- Keep warm and avoid exposure to wind or rain during the recovery period to prevent further illness.
- If symptoms persist, seek medical advice and consult a qualified professional.
How to Prevent Adverse Reactions from Gua Sha
- Every individual is different. Understand your own constitution and consult a professional to choose a gua sha method that suits you.
- Perform gua sha under the guidance of a trained practitioner. Avoid blind or self-administered techniques.
- Pay attention to diet before and after the session, and ensure your environment is stable—not too hot or cold.
- Control the frequency of gua sha treatments. Ideally, no more than 2–3 times per week, and less for certain sensitive individuals. Always allow the body to fully recover before the next session.
Gua sha has withstood the test of time for thousands of years, which proves its value and efficacy. However, while gua sha offers significant benefits, it is not one-size-fits-all. What works for others may not work for you. It’s equally important to acknowledge and understand post-treatment reactions—there’s no need for panic or anxiety.
Health starts with understanding yourself. Practice gua sha wisely and safely.