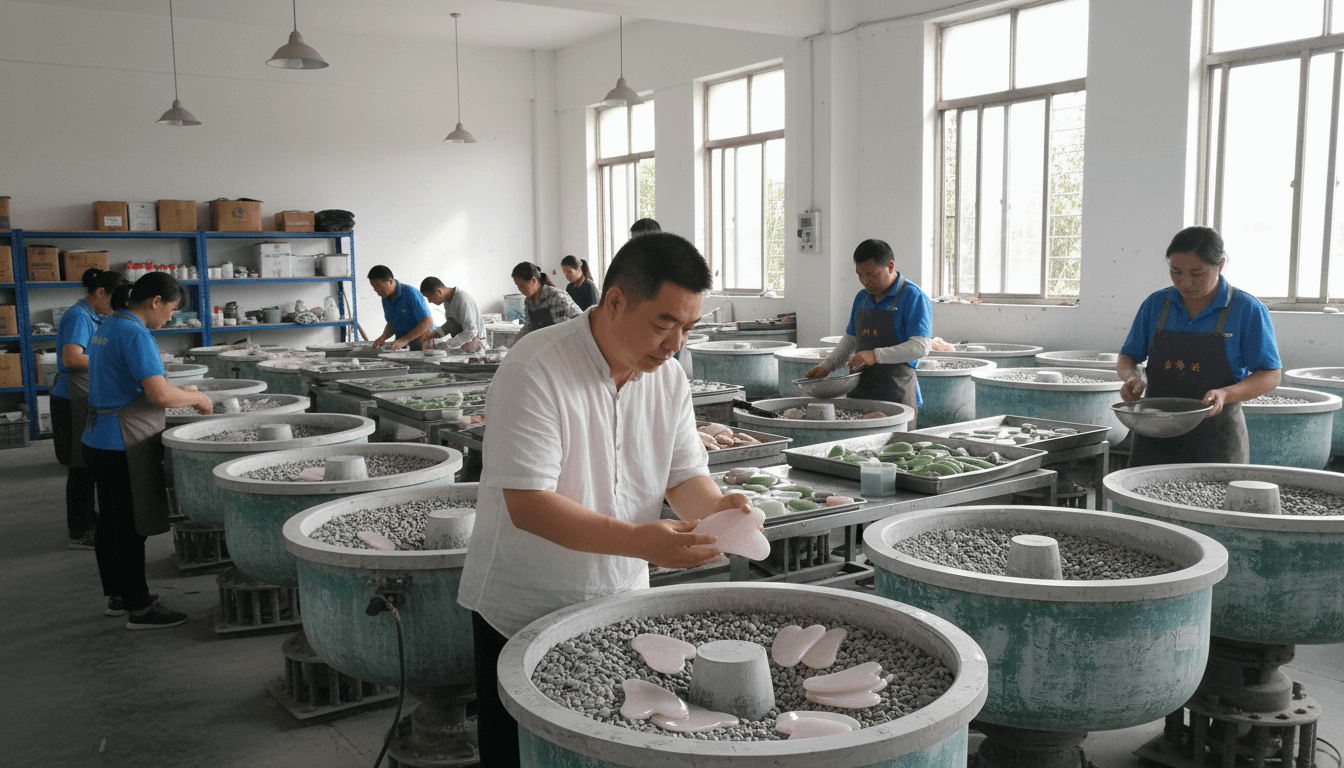

In today’s global wellness and beauty market, gua sha tools are widely available, yet their quality varies dramatically. For buyers, brands, and professionals, the real difference between an ordinary product and a premium one often lies in manufacturing details that are not immediately visible. Among these details, the polishing process stands out as one of the most decisive factors.
From the perspective of an experienced gua sha manufacturer, polishing is far more than a cosmetic step. It directly influences skin safety, tactile comfort, hygiene, durability, and long-term user trust. At Deyi Gems, where we have spent years working across gua sha production, wholesale supply, and OEM customization, polishing is treated as a core technical discipline rather than a finishing shortcut.
This article reveals the often-overlooked secrets behind the polishing process in gua sha manufacturing. By understanding how professional manufacturers approach polishing, buyers can better evaluate quality, while brands can make more informed sourcing decisions.
The Role of Polishing in Professional Gua Sha Manufacturing
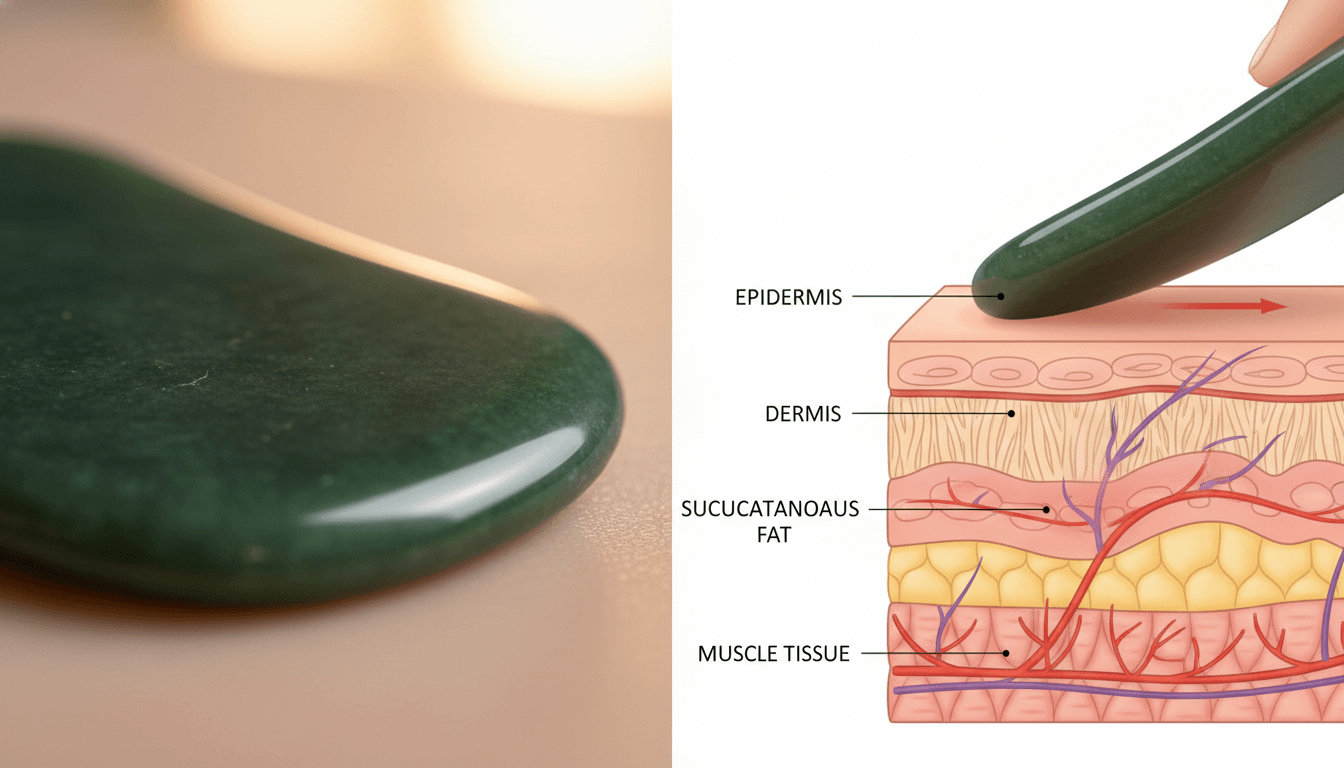
Polishing as a Functional, Safety-Critical Process
Many consumers associate polishing purely with visual shine. In reality, polishing is fundamentally a functional safety process. A properly polished gua sha tool reduces friction against the skin, prevents micro-scratches, and minimizes irritation during repeated use, especially on sensitive facial areas.
From an engineering standpoint, surface quality is measured using surface roughness (Ra values). According to ISO 4287 – Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS): Surface Texture, surface roughness directly affects friction, wear, and biological interaction with human skin
(Source: https://www.iso.org/standard/10132.html).
In cosmetic and skin-contact tools, professional manufacturers typically target Ra values ≤ 0.8 μm as a baseline, while premium gua sha tools often achieve Ra values between 0.2 and 0.4 μm through multi-stage mechanical polishing. These figures align with surface requirements commonly applied to dermatological and medical-grade instruments.
Why Polishing Reflects Manufacturing Capability
Almost any factory can cut stone or metal into a gua sha shape. However, consistent, high-level polishing requires skilled labor, calibrated equipment, and strict quality control. In professional gua sha manufacturing, polishing can account for 30–40% of total production labor time, especially for natural stone tools.
Factories that underinvest in polishing often produce tools with uneven edges, hidden micro-chips, or inconsistent thickness. These defects may not be obvious in product photos but become immediately noticeable during use, damaging both user experience and brand reputation.
Raw Materials and Their Influence on Polishing Techniques

Natural Stone Gua Sha: Beauty with Structural Complexity
Natural stones such as rose quartz, jade, green aventurine, and amethyst are widely used in gua sha tools due to their appearance and cultural value. However, natural stone is inherently non-uniform. Variations in grain structure, density, and internal micro-fractures significantly affect polishing outcomes.
For example, rose quartz typically ranks around 7 on the Mohs hardness scale, while nephrite jade ranges between 6 and 6.5. Harder stones require longer polishing cycles and finer abrasives to achieve skin-safe smoothness. A responsible gua sha manufacturer adjusts polishing parameters for each material batch rather than applying a generic process.
Failure to account for these variations can result in surface stress, edge chipping, or premature cracking during use.
Metal Gua Sha Tools and Precision Surface Control
Metal gua sha tools, particularly those made from stainless steel or copper, follow a different polishing logic. Medical-grade stainless steel used in cosmetic tools often aligns with standards such as ASTM F138 or ISO 5832, emphasizing corrosion resistance and surface smoothness.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) highlights that smooth, non-porous metal surfaces are easier to clean and less likely to retain microorganisms, which is why stainless steel is widely used in medical devices
(Source: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices).
For metal gua sha tools, polishing improves not only tactile comfort but also oxidation resistance and long-term durability, making it essential for professional-grade products.
The Step-by-Step Polishing Process in a Professional Gua Sha Factory
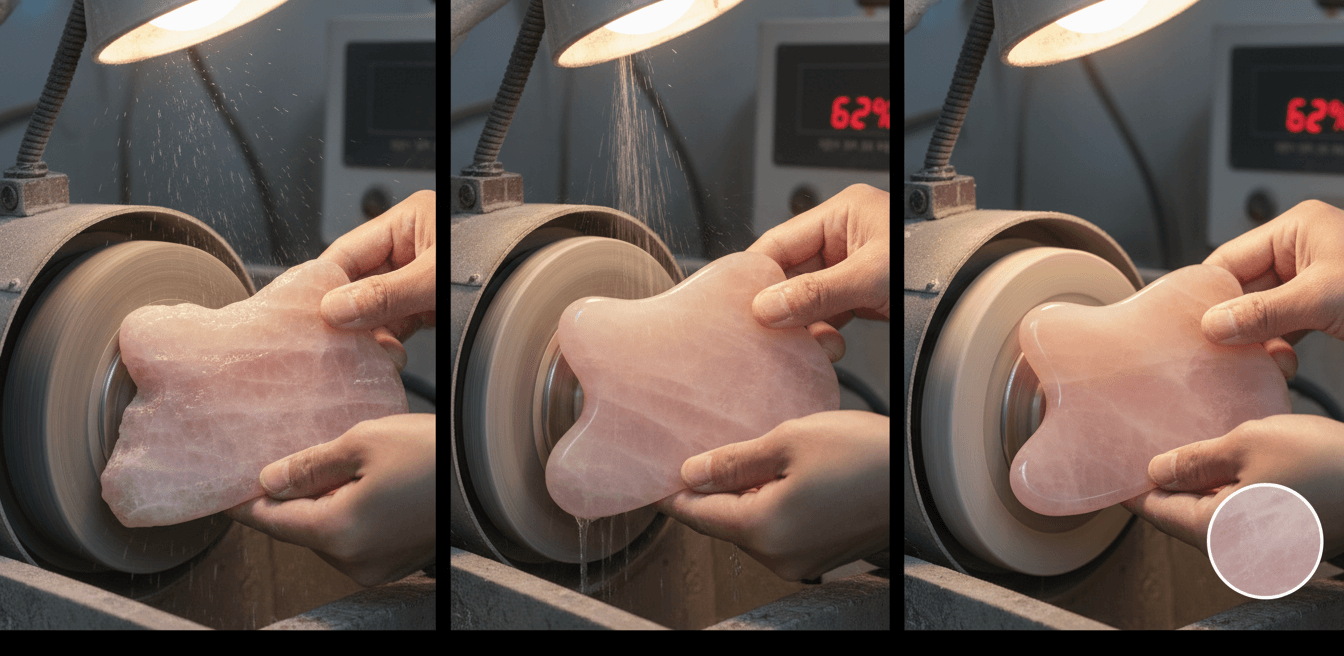
Rough Polishing: Structural Correction and Edge Safety
Rough polishing is the first stage following cutting and shaping. Its primary function is to remove visible tool marks, sharp edges, and surface irregularities. Coarse abrasive belts or wheels are typically used at this stage.
Precision is critical. Excessive pressure may cause micro-fractures in stone or deformation in metal, while insufficient pressure leaves deep scratches that compromise later stages. In professional factories, rough polishing maintains dimensional accuracy within ±0.3 mm, ensuring both safety and consistency.
Medium Polishing: Surface Refinement and Ergonomics
Medium polishing uses finer abrasives to refine surface texture and unify contours. This stage plays a major role in defining how the gua sha tool feels in hand and how it glides along facial and body contours.
Internal manufacturing data shows that medium polishing alone can reduce surface roughness by over 60% compared to rough-polished surfaces. Manufacturers who skip or rush this step often rely on surface coatings to compensate, which raises long-term safety concerns.
Fine Polishing: Achieving Skin-Contact Standards
Fine polishing is the final and most critical stage. Ultra-fine abrasives or polishing pastes are used to achieve the smoothness required for facial skin contact. At this stage, edges, curves, and contact points are carefully refined.
Industry best practices recommend that cosmetic tools show no detectable sharp edges under 10× magnification. High-end gua sha manufacturers routinely perform magnified inspections to eliminate micro-defects that could irritate the skin.
Hand Polishing vs Machine Polishing: A Manufacturer’s Perspective
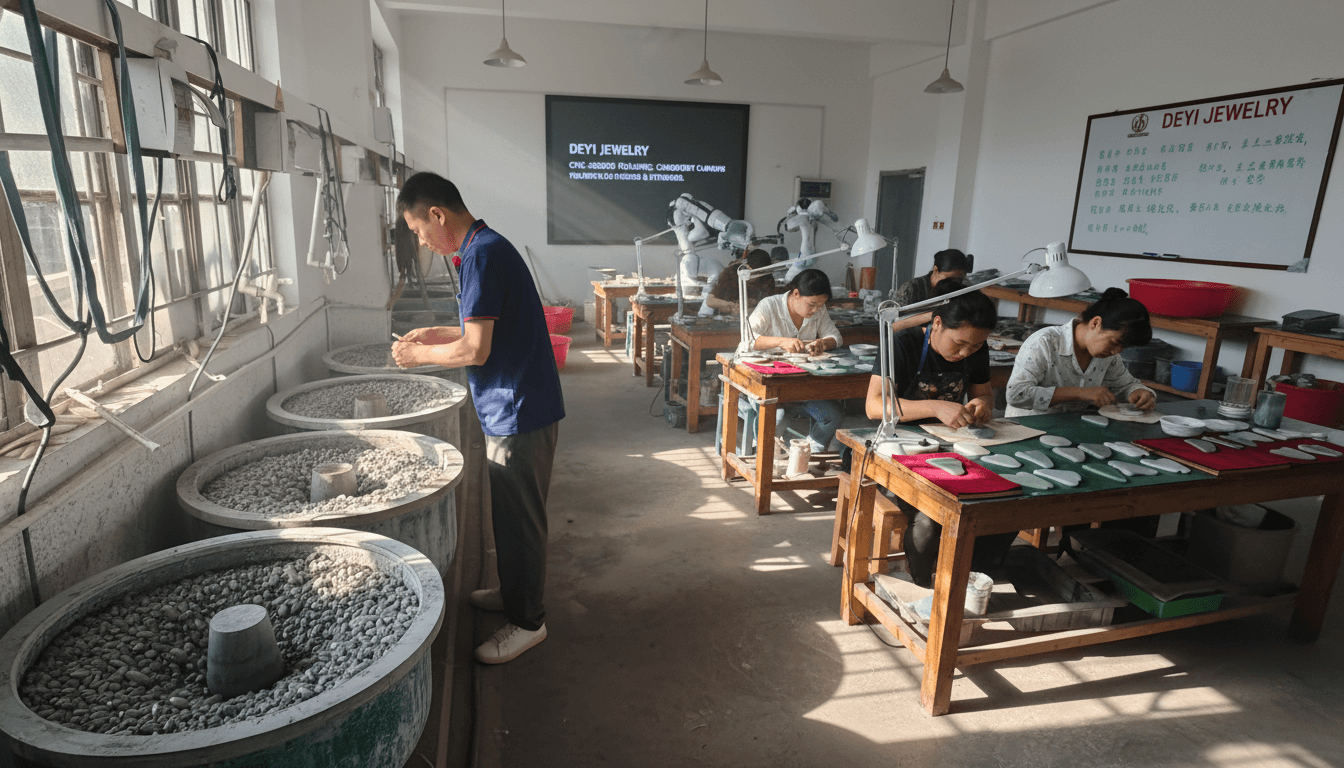

Machine Polishing for Scale and Consistency
Machine polishing offers efficiency and repeatability, making it suitable for large-scale production. CNC-assisted polishing equipment can maintain consistent curvature and thickness across standardized designs.
However, machines struggle with complex curves and organic shapes typical of traditional gua sha designs. Relying exclusively on machines often results in tools that look uniform but lack ergonomic refinement.
Hand Polishing for Precision and Human Judgment
Hand polishing introduces skilled human judgment into the process. Experienced workers can adjust pressure and motion based on tactile feedback, which is especially important for natural stone tools with invisible internal stress points.
At Deyi Gems, hand polishing is reserved for final finishing. Although it increases labor cost, it significantly reduces defect rates and improves overall comfort. Over time, hand-polished gua sha tools generate fewer complaints related to sharp edges or uneven surfaces.
Quality Control Standards Applied to Polishing
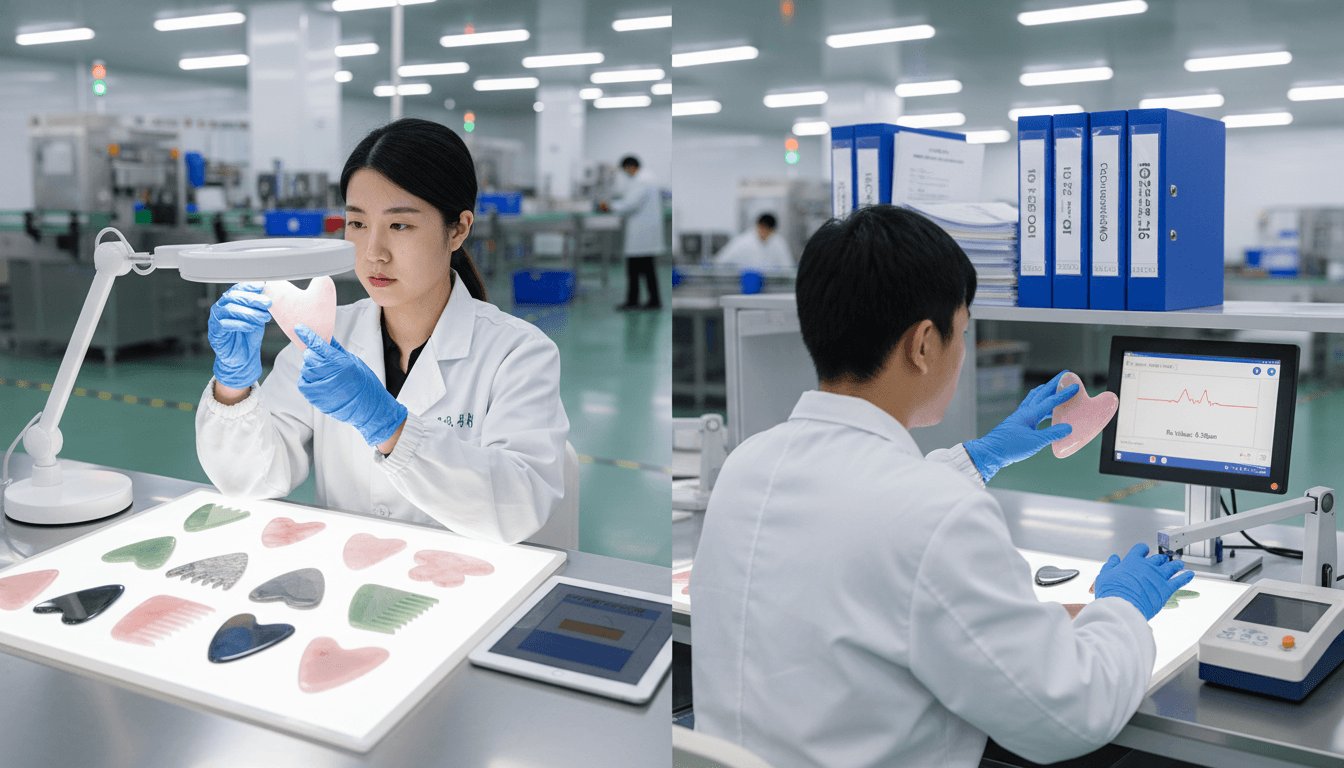

Visual and Tactile Inspection
Professional gua sha manufacturers implement multi-layer inspection protocols. Visual inspection identifies cracks, scratches, and color inconsistencies, while tactile inspection ensures smoothness and balance.
Well-trained inspectors can detect surface defects as small as 0.1 mm by touch alone. This level of sensitivity cannot be replaced entirely by automated systems.
Instrument-Based Surface Measurement
Advanced manufacturers use surface profilometers to verify Ra values. As discussed earlier, premium cosmetic tools often target Ra ≤ 0.4 μm.
Under ISO 22716 – Cosmetics: Good Manufacturing Practices, manufacturers are required to document and control processes that directly affect product safety and quality
(Source: https://www.iso.org/standard/36437.html).
Polishing is explicitly considered a critical process step for skin-contact tools.
Polishing, Hygiene, and Microbial Safety
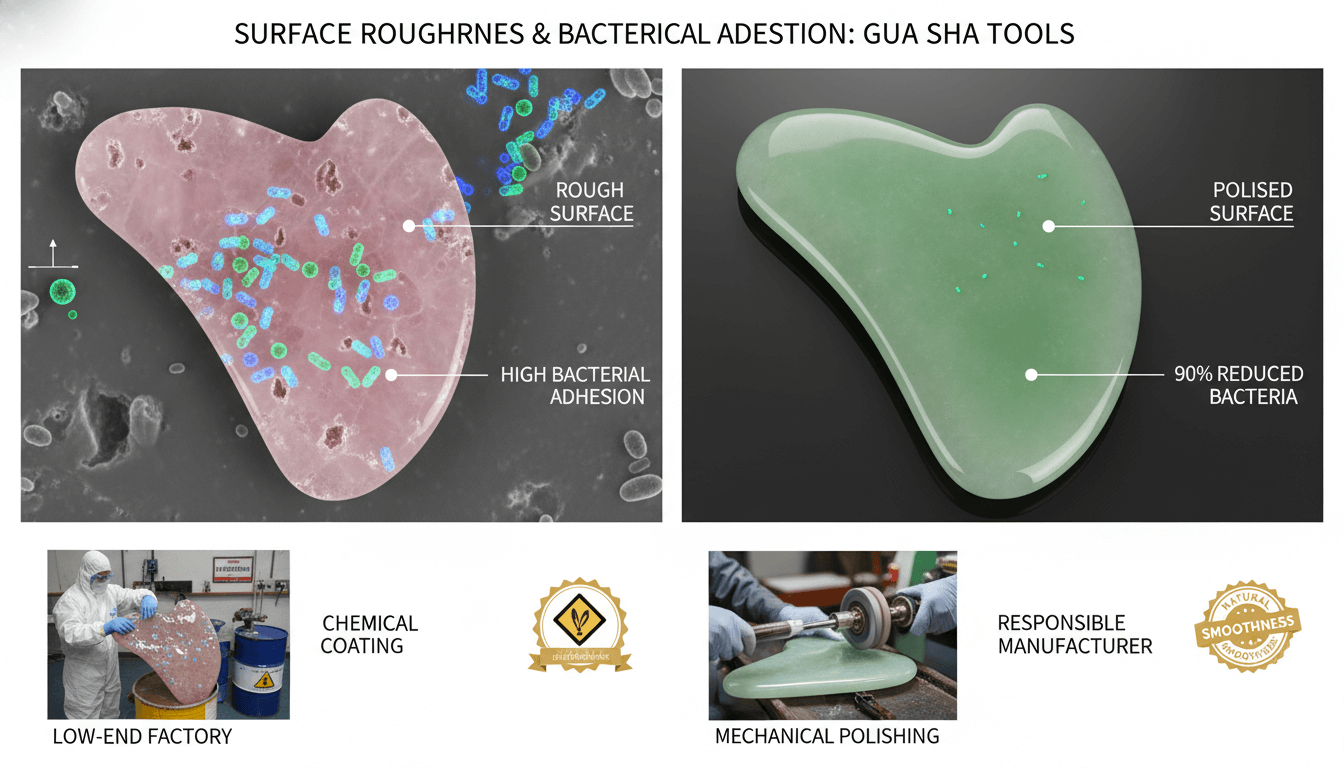
Surface Roughness and Bacterial Adhesion
Scientific research consistently shows that smoother surfaces reduce bacterial attachment. Studies indexed by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) demonstrate that lowering surface roughness can reduce bacterial adhesion by up to 90%, particularly on non-porous materials such as stainless steel and polished stone
(Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452227/).
For gua sha tools used repeatedly on the face, this relationship makes fine polishing essential for hygiene, not optional.
Mechanical Polishing vs Chemical Coatings
Some low-end factories rely on chemical glazing or surface coatings to create artificial shine. While visually appealing, these coatings may degrade, peel, or react with skincare products over time.
Under the EU REACH regulation, unnecessary chemical treatments in consumer products are strictly regulated, especially for items with prolonged skin contact
(Source: https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach).
Responsible gua sha manufacturers prioritize mechanical polishing to achieve natural smoothness while minimizing chemical exposure risks.
How Polishing Shapes User Experience and Brand Value
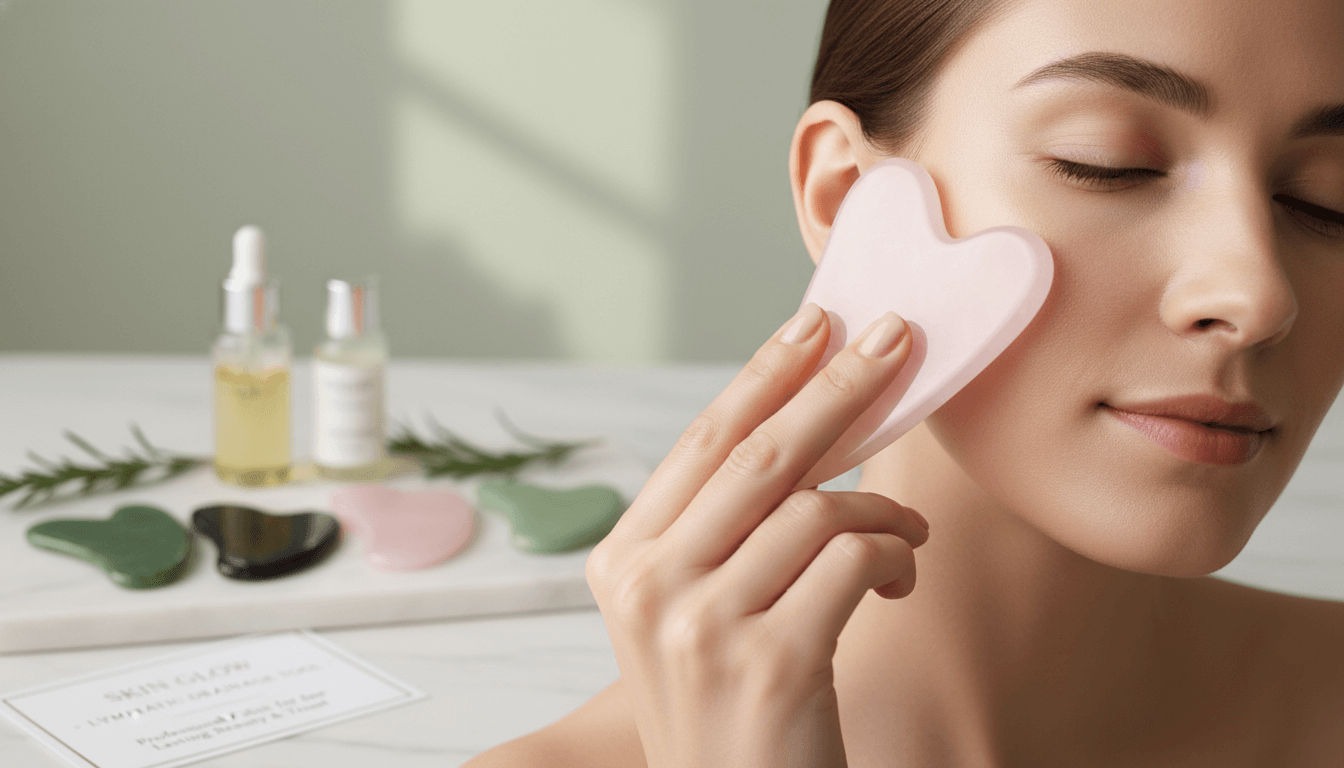

Skin Feel and Treatment Effectiveness
A well-polished gua sha tool glides smoothly without requiring excessive pressure. This improves lymphatic drainage and microcirculation while reducing the risk of irritation or redness.
Customer feedback consistently shows that superior polishing correlates with higher satisfaction and lower return rates, particularly for facial gua sha tools.
Durability and Long-Term Appearance
Polishing also determines how a tool ages. Poorly polished tools develop scratches and dullness quickly, while properly polished surfaces maintain their finish even after repeated use and cleaning.
For wholesale buyers and private-label brands, this durability translates into fewer after-sales issues and stronger long-term brand trust.
Common Polishing Mistakes Made by Inexperienced Manufacturers
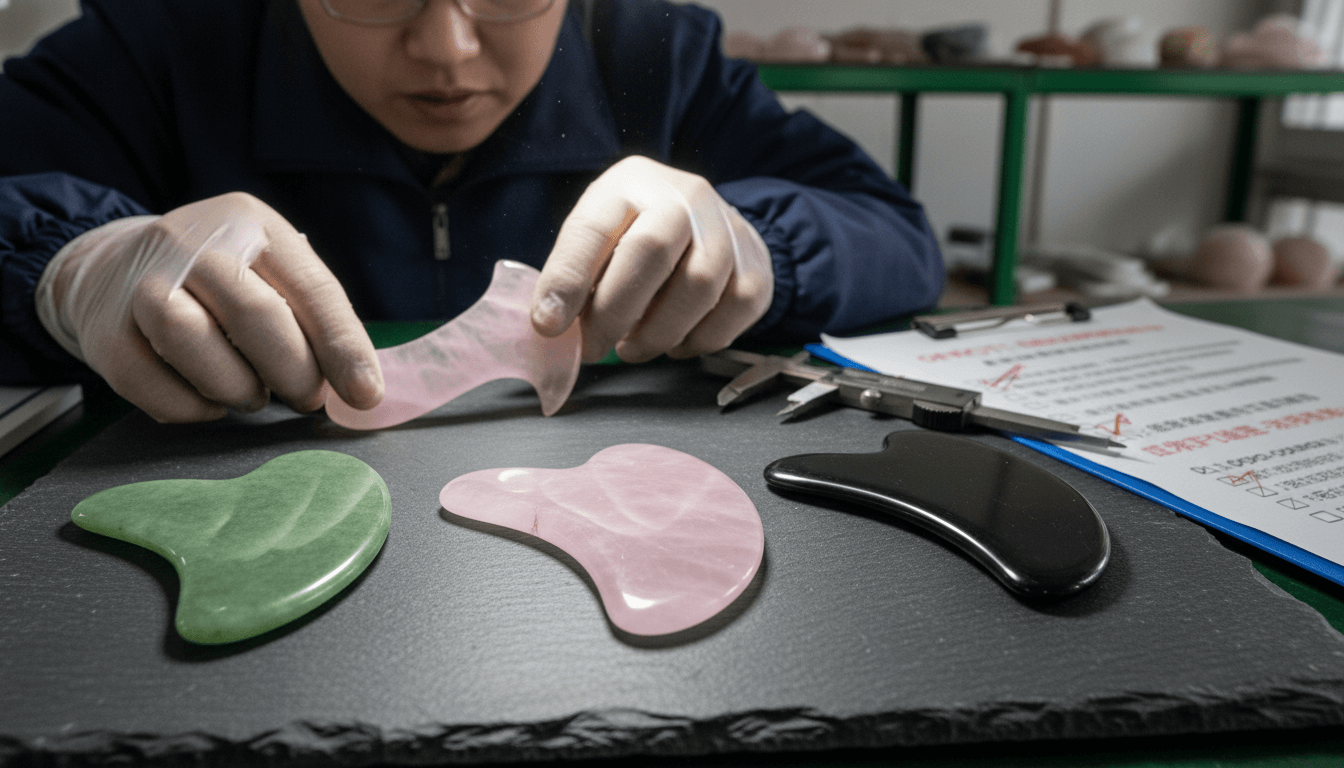

Over-Polishing and Structural Weakness
Excessive polishing can thin edges and distort intended shapes. This weakens structural integrity and compromises functionality.
Professional manufacturers carefully monitor material loss during polishing to ensure thickness remains within safe tolerances.
Inconsistent Edge Finishing
Edges are the most critical skin-contact areas. Inconsistent polishing often results in sharp corners or uneven curves, increasing the risk of discomfort.
This issue is one of the most frequent defects identified during factory audits for OEM and ODM projects.
Choosing a Gua Sha Manufacturer Based on Polishing Expertise
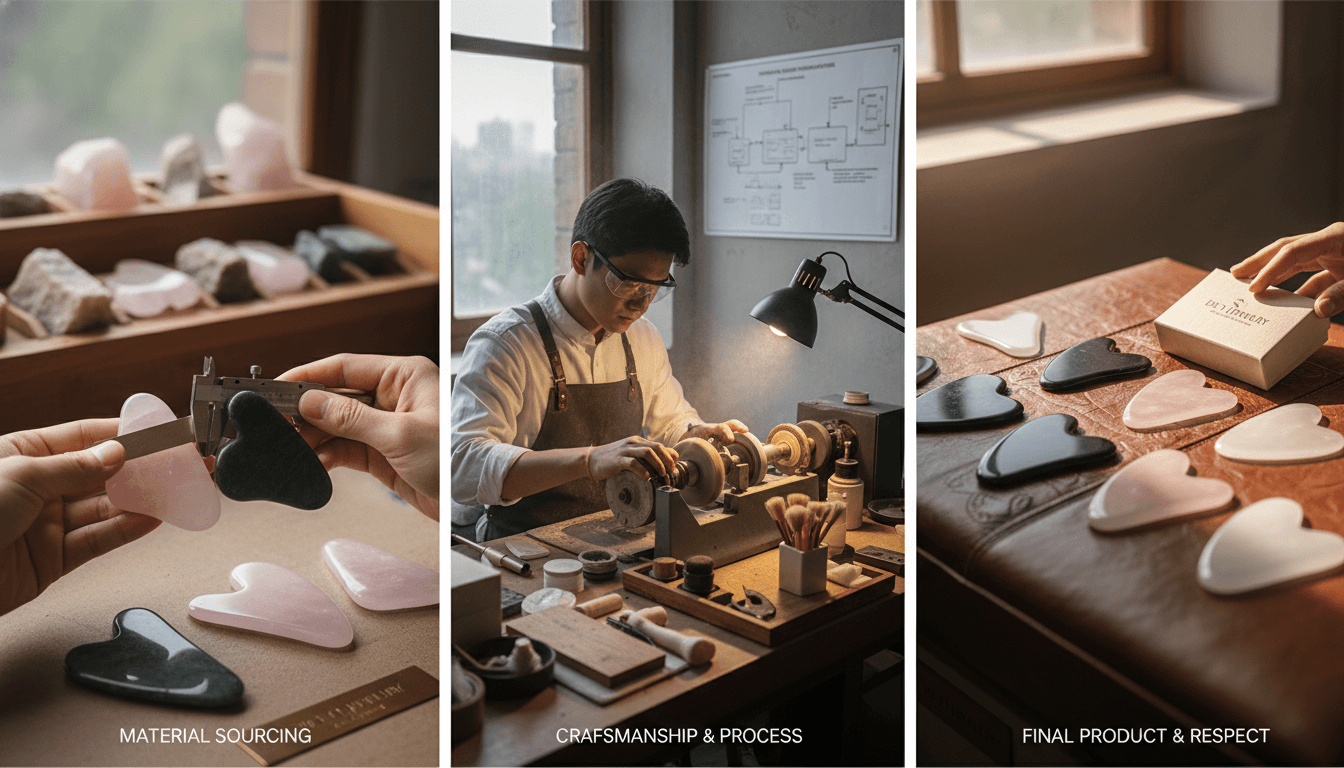

What Buyers Should Evaluate
Buyers should ask detailed questions about polishing methods, inspection standards, and worker training. A professional gua sha manufacturer can clearly explain each polishing stage and its purpose.
Vague answers or an exclusive focus on appearance rather than safety often indicate inadequate manufacturing depth.
Polishing as a Reflection of Manufacturing Philosophy
Polishing reflects how a factory values detail, craftsmanship, and end users. Manufacturers who invest in proper polishing usually apply the same standards to material sourcing, cutting, and packaging.
At Deyi Gems, polishing represents respect—for the material, the skin, and the brand that stands behind every product.
Conclusion: Polishing as the Hidden Signature of a True Gua Sha Manufacturer
In the increasingly competitive gua sha market, polishing remains one of the clearest indicators of manufacturing integrity. It directly affects safety, hygiene, comfort, and long-term performance, making it a defining competency rather than a visual enhancement.
For brands, retailers, and professionals, understanding polishing processes helps distinguish true gua sha manufacturers from surface-level suppliers. Behind every smooth, skin-safe gua sha tool is a carefully controlled polishing process shaped by experience, standards, and respect for the end user.
As the industry continues to mature, polishing will remain a quiet but unmistakable signature of manufacturers who take their craft seriously.




