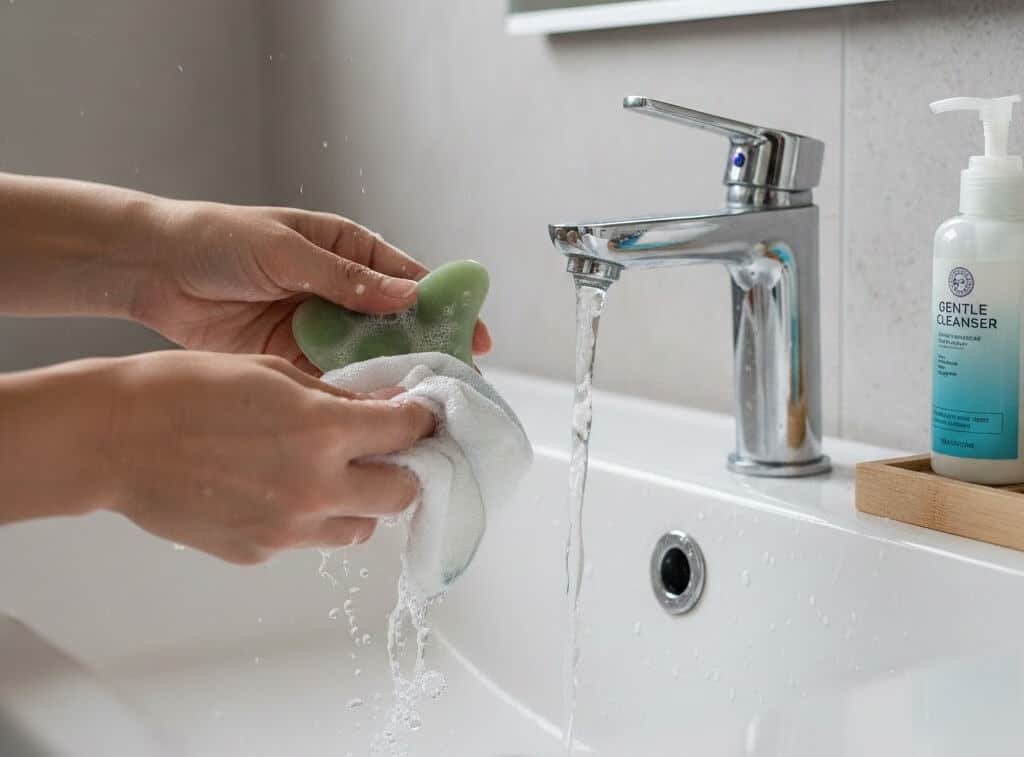

In both professional wellness settings and daily personal skincare routines, Gua Sha tools are used in direct contact with the skin. From a manufacturer and wholesale perspective, proper cleaning is not only about hygiene, but also about material protection, product longevity, and regulatory compliance. At Deyi Gems, with years of experience in Gua Sha production and global wholesale supply, we have observed that incorrect cleaning methods are one of the most common reasons for premature product damage and customer complaints.
Different Gua Sha materials react very differently to water, oils, detergents, alcohol, and temperature changes. A jade Gua Sha board, for example, cannot be cleaned in the same way as stainless steel or resin. Understanding these differences is essential for wholesalers, brands, spas, and end users alike. This article focuses on how to use gua sha tools, explaining correct methods for different materials while providing authoritative data and standards to support best practices.
- Understanding Gua Sha Tool Cleaning as a Core Usage Practice
- Material Differences: Why One Cleaning Method Does Not Fit All
- How to Clean Jade Gua Sha Tools Safely
- How to Clean Rose Quartz Gua Sha Tools Properly
- Cleaning Black Obsidian Gua Sha Tools
- Stainless Steel Gua Sha Tools: Industrial Hygiene Advantages
- Resin and Acrylic Gua Sha Tools: Cleaning Without Surface Damage
- Glass Gua Sha Tools and Their Cleaning Requirements
- The Role of Clean Gua Sha Frequency in Gua Sha Tool Longevity
- Drying and Storage After Cleaning
- Common Cleaning Mistakes Seen in Wholesale Feedback
- Why Brands and Wholesalers Must Provide Clear Cleaning Instructions
- Conclusion: How to Clean Gua Sha Tool as a Professional Standard
Understanding Gua Sha Tool Cleaning as a Core Usage Practice

Why Cleaning Is a Functional Part of Gua Sha Usage
Gua Sha is not a disposable skincare practice. Each tool is designed for repeated use over months or even years. During use, the tool comes into contact with facial oils, massage creams, sweat, and exfoliated skin cells. If residue accumulates, it can reduce glide performance, affect skin comfort, and increase the risk of bacterial growth.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), non-porous personal care tools that contact skin should be cleaned after each use to reduce microbial contamination. While Gua Sha tools are not medical devices, this hygiene principle still applies, especially in spa or professional environments. Source: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol
Hygiene, Brand Trust, and Wholesale Standards
From a wholesale and brand standpoint, clean gua sha tool guidance is part of product responsibility. Clear cleaning instructions reduce product returns, extend service life, and help brands comply with consumer safety expectations. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) emphasizes truthful usage and care instructions for consumer products to prevent misleading claims. Source: https://www.fda.gov/consumers
Material Differences: Why One Cleaning Method Does Not Fit All

Natural Stone vs. Man-Made Materials
Gua Sha tools can be broadly divided into natural stone materials and engineered materials. Natural stones such as jade, rose quartz, and obsidian are formed with microscopic pores and natural fissures. Man-made materials such as stainless steel, resin, and glass are more uniform and generally less porous.
This structural difference directly affects water absorption, resistance to chemicals, and tolerance to temperature. Ignoring these material properties during cleaning can lead to cracking, discoloration, or surface dulling.
Porosity and Absorption Explained
According to geological material studies published by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), many natural stones exhibit micro-porosity even when polished. These pores are invisible to the naked eye but can absorb oils and moisture over time. Source: https://www.usgs.gov
How to Clean Jade Gua Sha Tools Safely

Characteristics of Jade Relevant to Cleaning
Jade, including nephrite and jadeite, is valued for its density and smoothness. However, despite its hardness, jade can still absorb oils through micro-pores. Excessive soaking or harsh detergents may weaken the stone over time.
In manufacturing, jade Gua Sha tools are usually polished to a mirror finish, but polishing does not eliminate internal porosity. This makes gentle cleaning essential.
Recommended Cleaning Method for Jade Gua Sha
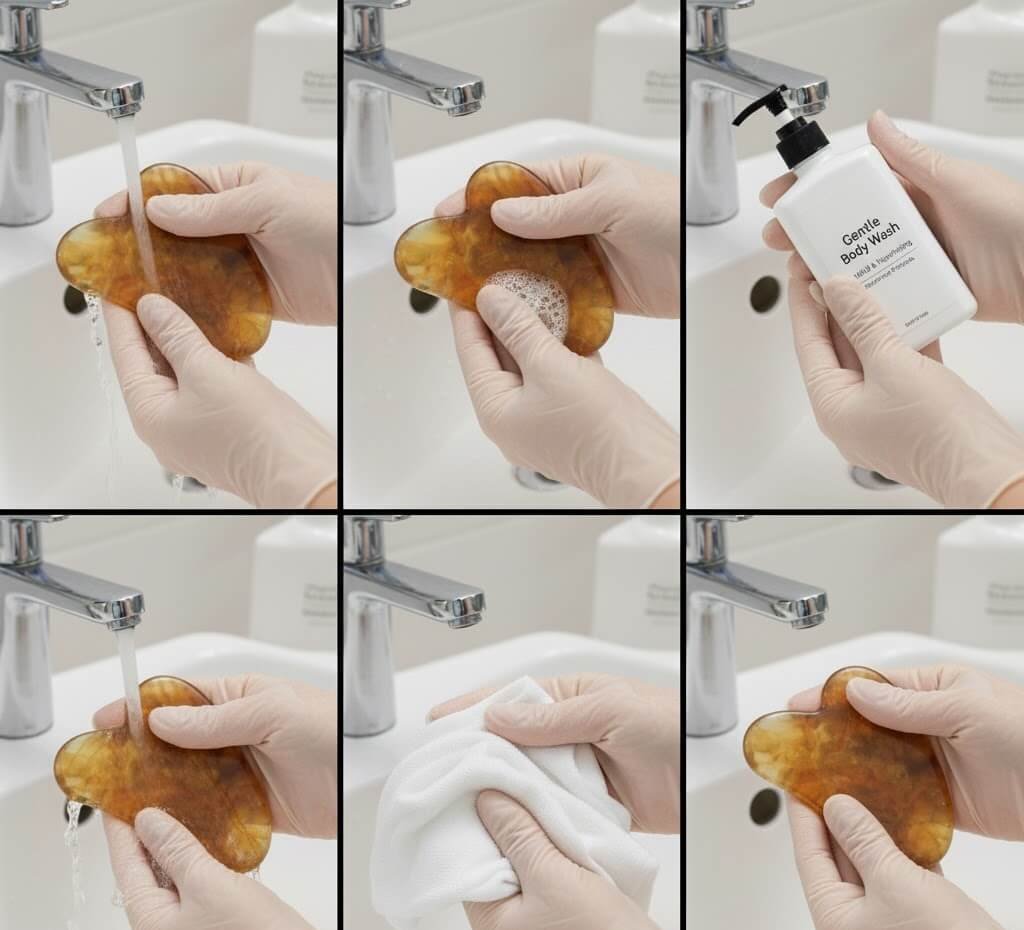
For daily clean gua sha tools, lukewarm water combined with a mild, fragrance-free soap is sufficient. The tool should be rinsed quickly and wiped dry with a soft cotton cloth. Prolonged soaking is not recommended, as water penetration can cause internal stress.
According to material care guidance from the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), jade should never be exposed to harsh chemicals or ultrasonic cleaners. Source: https://www.gia.edu
How to Clean Rose Quartz Gua Sha Tools Properly
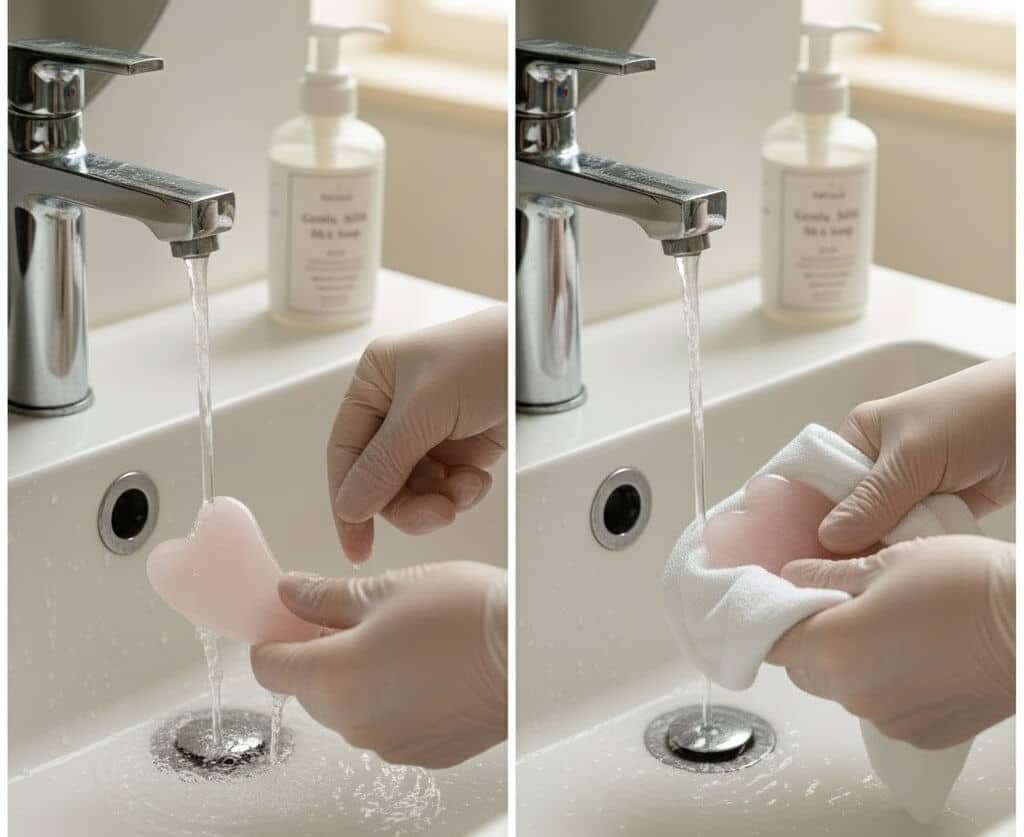

Material Properties of Rose Quartz
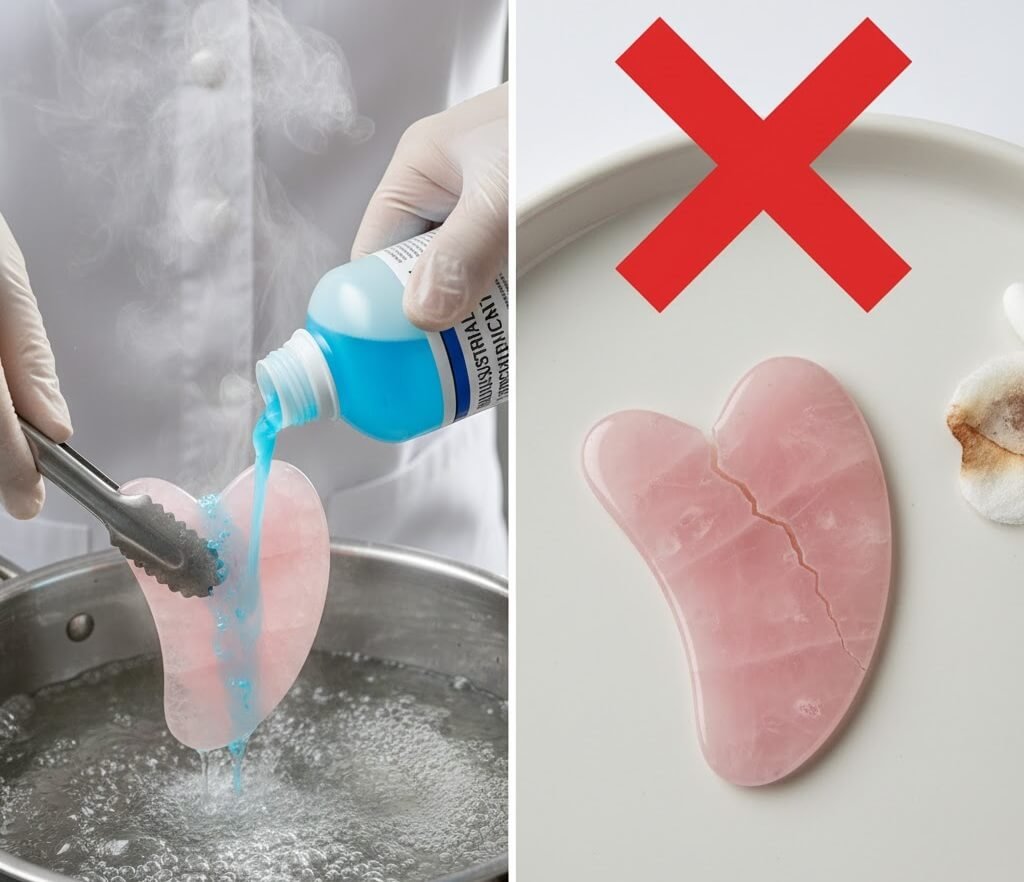
Rose quartz is a crystalline form of silicon dioxide with a Mohs hardness of approximately 7. While relatively hard, it is more brittle than jade and prone to internal fractures when exposed to sudden temperature changes.
From a wholesale perspective, rose quartz tools often receive complaints related to cracking caused by improper cleaning or storage.
Cleaning Best Practices for Rose Quartz
Rose quartz Gua Sha tools should be cleaned using warm water and a mild cleanser, similar to jade. Alcohol-based disinfectants should be avoided for frequent use, as they may dull the surface polish over time.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) notes that overuse of alcohol on consumer-grade tools can degrade surface finishes, even when microbial reduction is achieved. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Cleaning Black Obsidian Gua Sha Tools
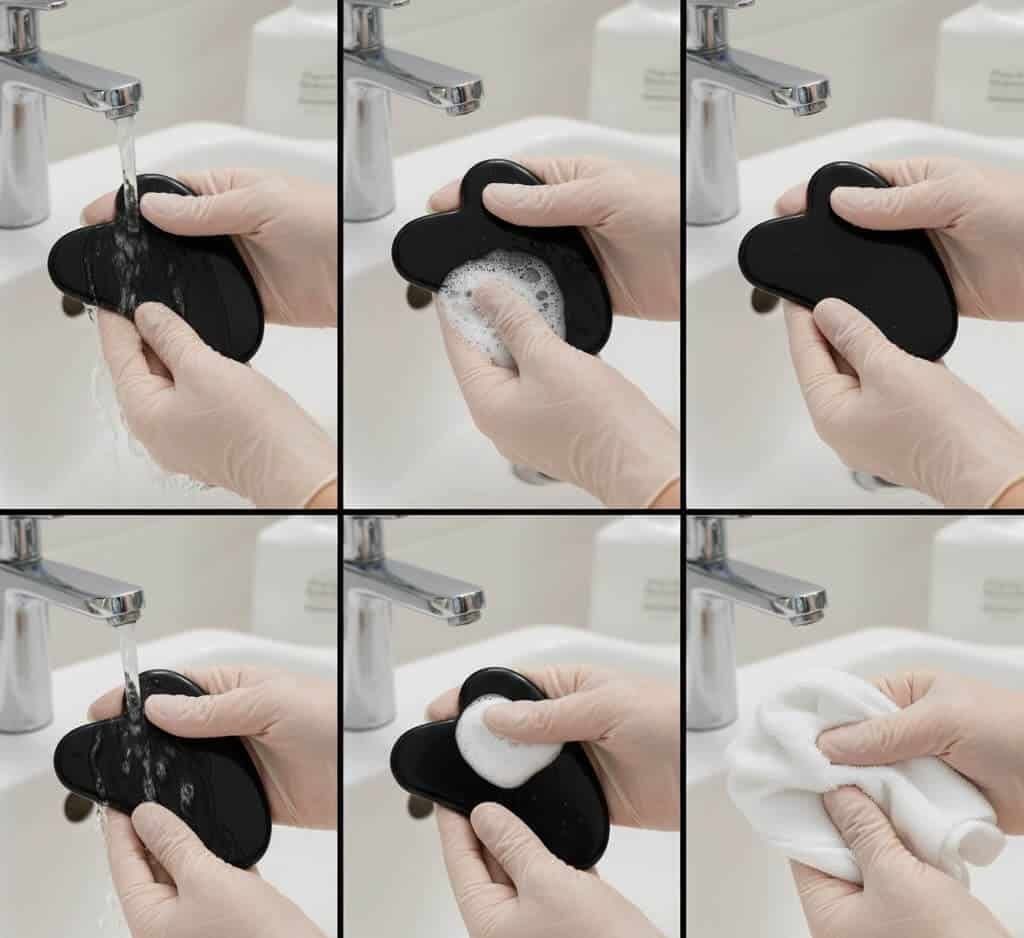

Why Obsidian Requires Extra Care
Obsidian is volcanic glass, not a crystalline stone. While it appears solid, its internal structure is glass-like and can be sensitive to impact and temperature shock. This makes cleaning practices especially important.
Unlike jade or quartz, obsidian is less porous but more brittle, meaning physical handling matters as much as chemical exposure.
Proper Cleaning Approach for Obsidian
A soft cloth dampened with water is often sufficient for routine cleaning. Mild soap can be used occasionally, but the tool should never be soaked or exposed to boiling water. Abrasive sponges must be avoided, as they can cause micro-scratches.
Stainless Steel Gua Sha Tools: Industrial Hygiene Advantages
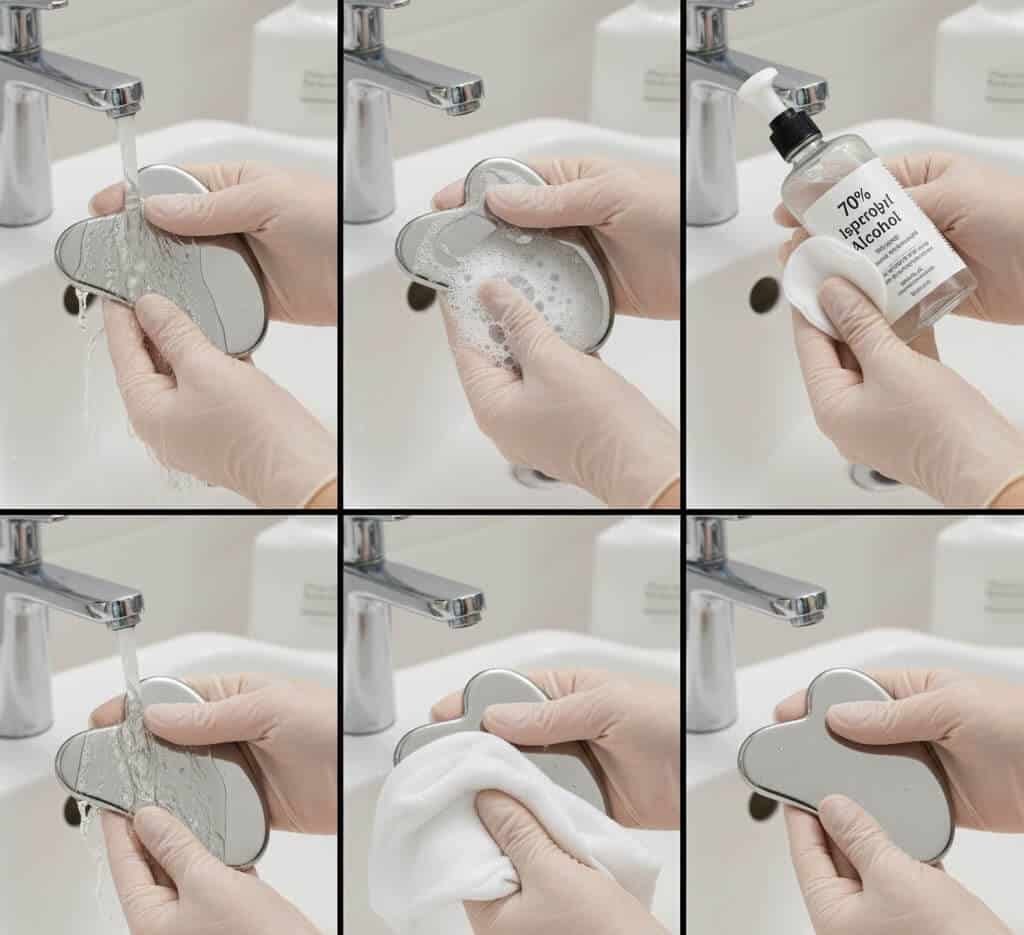
Why Stainless Steel Gua Sha Is Easier to Clean
Stainless steel Gua Sha tools are increasingly popular in professional settings due to their non-porous surface and high resistance to corrosion. Medical-grade stainless steel, such as 304 or 316L, does not absorb oils or bacteria.
According to ISO 7153-1 standards, stainless steel used in surgical instruments demonstrates high resistance to repeated cleaning and disinfection cycles. Source: https://www.iso.org
Cleaning and Disinfection for Stainless Steel
Stainless steel Gua Sha tools can be cleaned with warm water, soap, and even alcohol-based disinfectants without damage. For spa environments, they can be sanitized between clients using 70% isopropyl alcohol, which the CDC identifies as effective against most surface pathogens.
This durability significantly reduces maintenance concerns for wholesalers and professional buyers.
Resin and Acrylic Gua Sha Tools: Cleaning Without Surface Damage

Understanding Resin-Based Materials
Resin and acrylic Gua Sha tools are synthetic materials designed to mimic stone aesthetics at a lower cost. While non-porous, they are more sensitive to heat and chemical solvents.
Improper cleaning can lead to surface clouding, discoloration, or micro-cracks, especially in lower-grade resin products.
Recommended Clean Resin and Acrylic Gua Sha Practices
Resin tools should be cleaned using lukewarm water and a gentle soap. Alcohol, acetone, and essential oil solvents should be avoided, as they may degrade the polymer structure over time.
Material safety data sheets (MSDS) for cosmetic-grade resins confirm reduced chemical resistance compared to metals. Source: https://www.osha.gov
Glass Gua Sha Tools and Their Cleaning Requirements

Why Glass Is Chemically Stable but Physically Fragile
Glass Gua Sha tools are completely non-porous and chemically stable, making them hygienic and easy to clean. However, glass is sensitive to impact and thermal shock.
Sudden temperature changes during cleaning can cause cracking, even if the glass appears thick and durable.
Safe How to Clean Gua Sha Guidelines for Glass
Warm water and mild soap are sufficient for daily clean gua sha tools. Glass tools can tolerate alcohol disinfection but should never be exposed to boiling water or rapid cooling.
The Role of Clean Gua Sha Frequency in Gua Sha Tool Longevity

Daily Use vs. Professional Use
For personal daily use, cleaning after each session is recommended to prevent oil buildup. In professional spa environments, tools should be cleaned and disinfected between clients to meet hygiene expectations.
According to spa hygiene guidelines published by professional esthetics associations, reusable tools must undergo cleaning after every client interaction. Source: https://www.ascpskincare.com
Over-Cleaning Can Also Be Harmful
While cleanliness is essential, excessive use of strong disinfectants can shorten the lifespan of natural stone tools. Balance is key, especially for jade and quartz products.
Drying and Storage After Cleaning

Why Drying Is as Important as Washing
Residual moisture trapped on or inside a Gua Sha tool can cause long-term material degradation, especially in natural stone. Drying prevents water spots, mineral deposits, and microbial growth.
Soft, absorbent cloths are recommended over air drying for stone tools.
Storage Conditions That Support Hygiene
Tools should be stored in dry, ventilated environments away from direct sunlight. High humidity environments can accelerate material aging, particularly for jade and resin products.
Common Cleaning Mistakes Seen in Wholesale Feedback

Soaking Tools for Extended Periods
Extended soaking is one of the most common mistakes reported by wholesale clients. This practice increases water absorption in stone tools and can cause cracking months later.
Using Household Disinfectants Incorrectly
Bleach, vinegar, and abrasive cleaners are sometimes used by consumers, despite being unsuitable for most Gua Sha materials. These substances can permanently damage surfaces and void product warranties.
Why Brands and Wholesalers Must Provide Clear Cleaning Instructions
Reducing Returns and Customer Complaints
Clear, material-specific cleaning instructions significantly reduce product damage claims. At Deyi Gems, we have observed a measurable reduction in after-sales issues when detailed care guidance is included.
Supporting Compliance and Consumer Trust
Regulatory bodies such as the FTC emphasize accurate product usage information to prevent misleading consumers. Proper cleaning instructions are part of this responsibility. Source: https://www.ftc.gov
Conclusion: How to Clean Gua Sha Tool as a Professional Standard
Gua Sha tool cleaning is not a minor afterthought, but a core part of correct Gua Sha usage. Different materials require different care approaches, and understanding these differences protects both the user’s skin and the tool itself. From jade and rose quartz to stainless steel and resin, each material demands respect for its physical properties.
For brands, wholesalers, and professional buyers, educating customers about proper cleaning enhances product longevity, brand reputation, and regulatory compliance. At Deyi Gems, we believe that well-informed usage is as important as high-quality manufacturing, and proper cleaning is where both meet.




